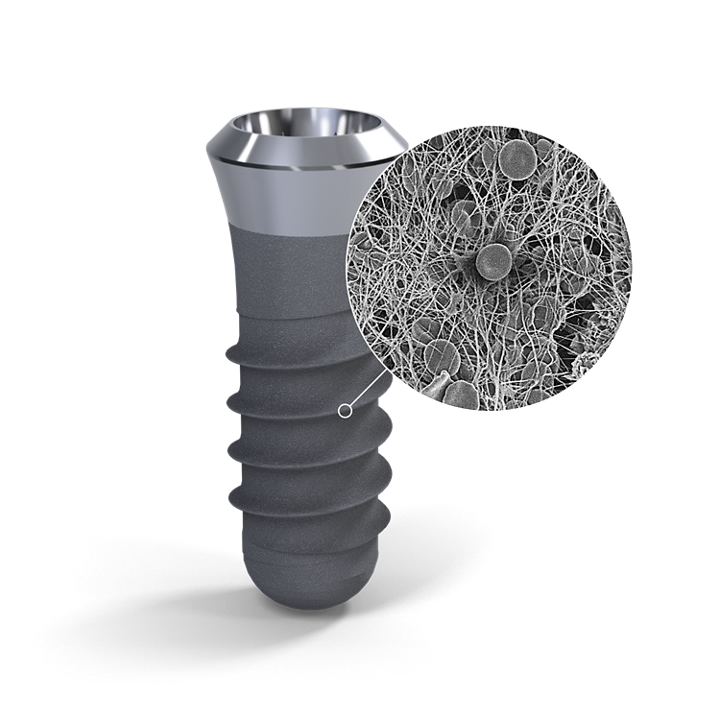
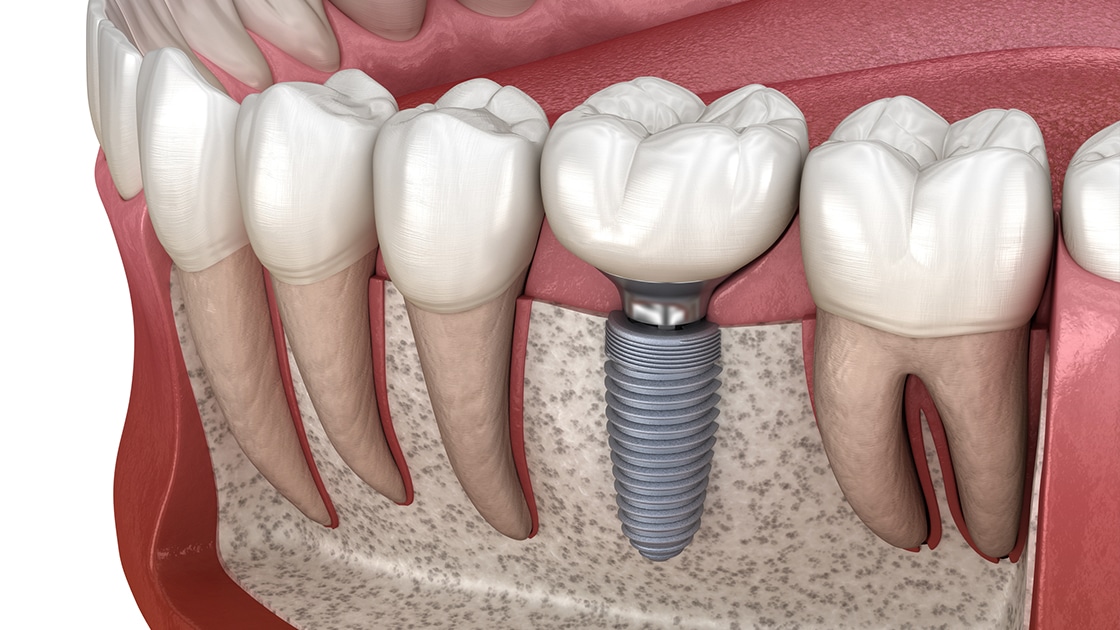
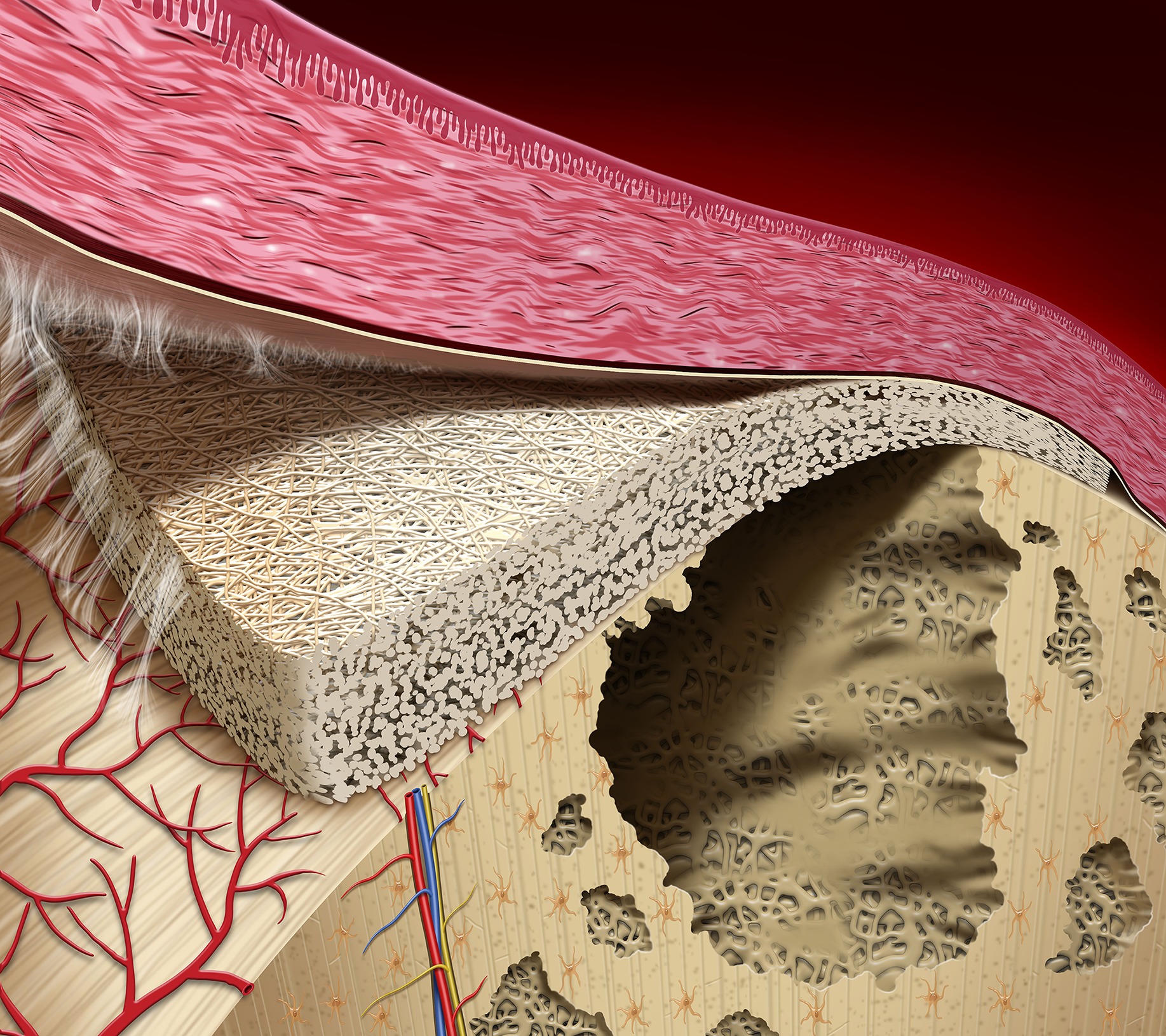
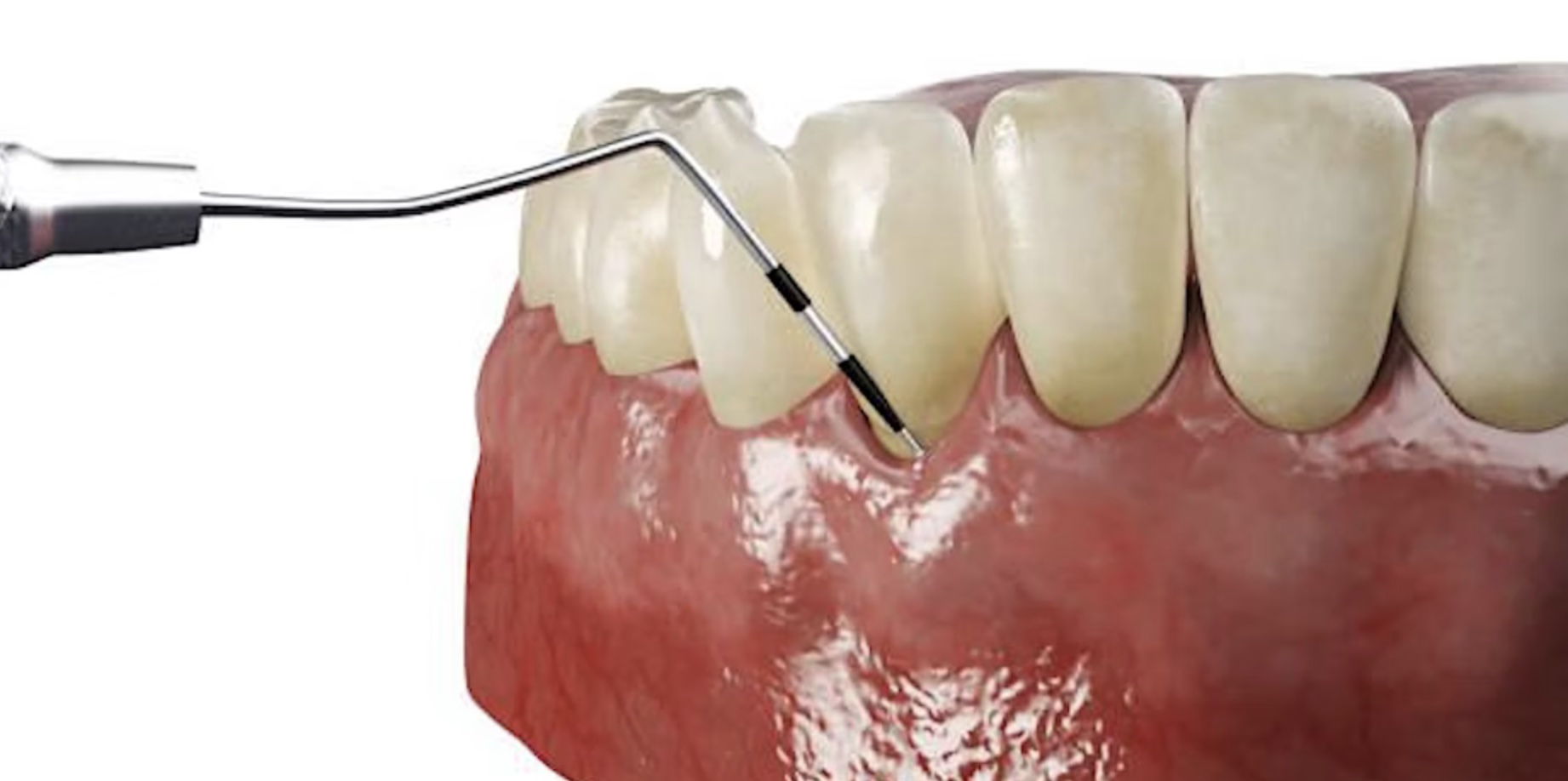
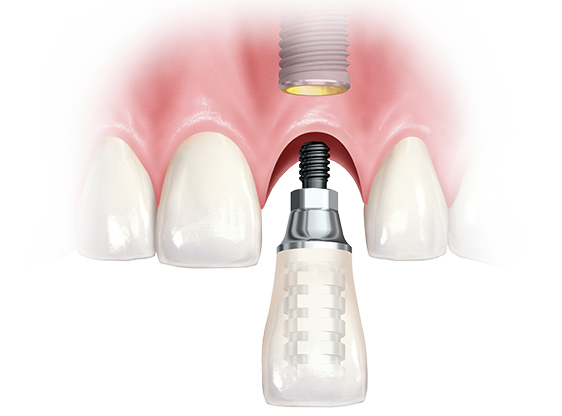
Implant supported posterior restorations
Considerations for fabrication of implant- supported posterior restorations Chiche et al 1991 Implant supported prosthesis are a excellent alternative for patients who are reluctant to use RPDs. Implant restorations may be either screw retained or cemented. Cemented prosthesis offer simplicity and good control of morphology but can be considered if removal or no re-servicing is