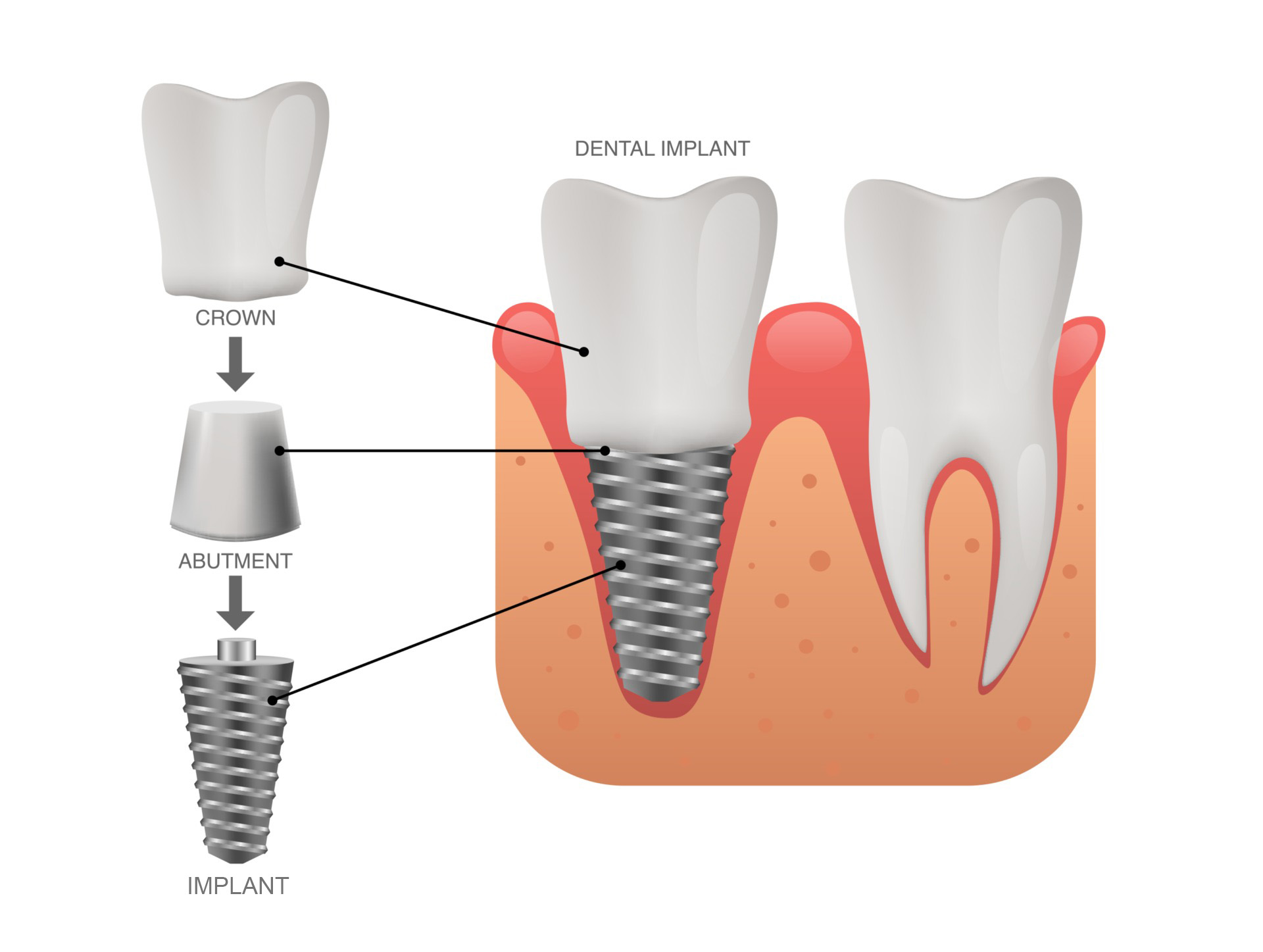
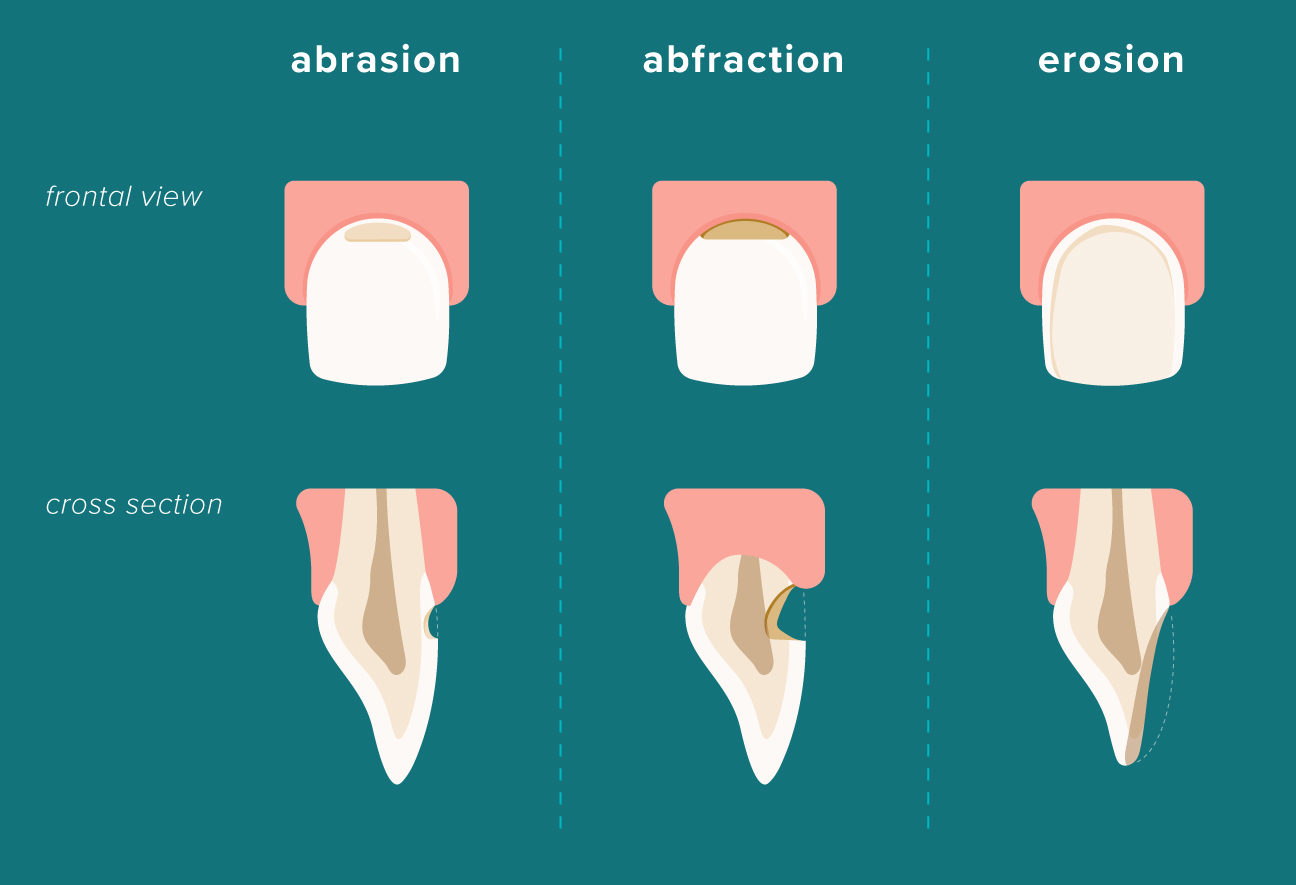
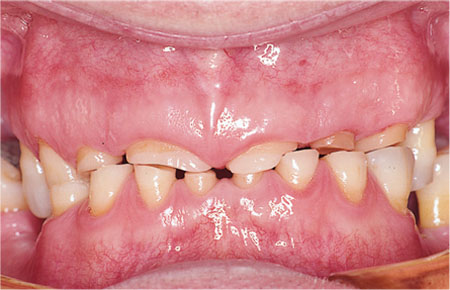
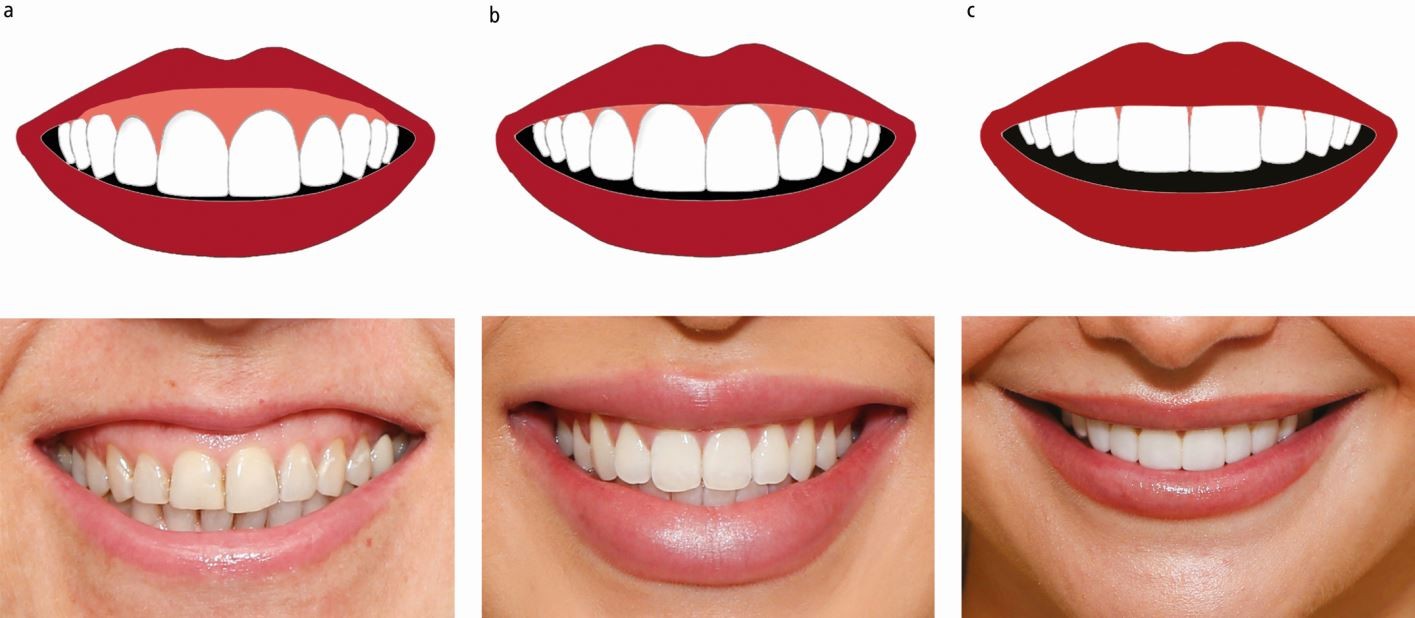
Centric relation recording techniques
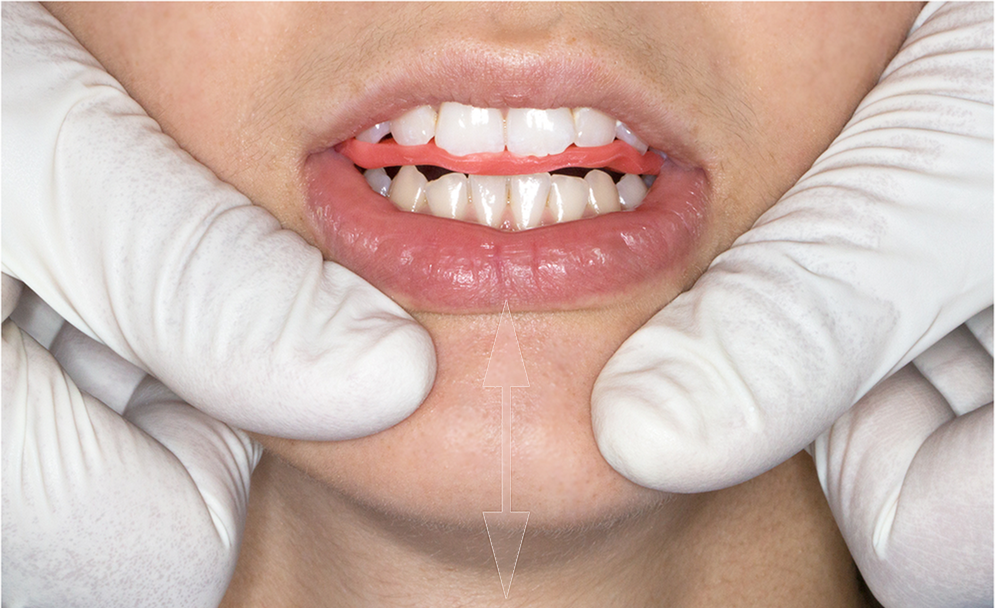
Centric relation recording techniques- A comparative investigation Kantor et al 1972. J. Prosthet. Dent Centric relation Maxillo-mandibular relationship, independent of tooth contact, in which the condyles articulate in the anterior-superior position against the posterior slopes of the articular eminences. JPT9 This paper studied at the different in what investigators report on an assessment of four