- By - Malfaifi
- Posted on
- Posted in Fixed, Prosthesis, Removable
The golden proportion revisited
The Golden Proportion Revisited
J. Preston 1993
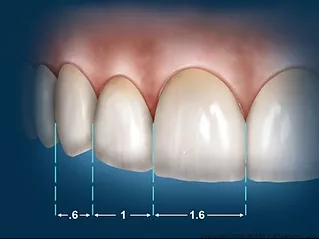
- In an attempt to seek mathematical assistance in developing dental esthetics, Levin advocated the use of the golden proportion for establishing tooth size and stated that “the perceived width of the maxillary central incisor is in golden proportion to the width of the lateral incisor” (1:0.618).
- Similarly he found that “the width of the maxillary lateral incisor is in golden proportion to the width of the canine.” (this proportion was derived from the apparent size-viewed directly from the anterior).
- He devised a grid with the spaces in golden proportion and advocated the use of this grid to evaluate and develop the harmonious proportions of teeth.
- The current article investigates the validity of the golden proportion in dental esthetics.
Material and Methods:
1. Orthodontic casts of 58 second-year dental students at the University of Southern California were obtained.
2. Individual images were made of the maxillary and mandibular casts
3. An image measurement program (OrthoCeph) was used to measure the apparent mesio-distal width of all the teeth from the right canine to the left second molar.
4. Ratios investigated were evaluated as being within 0.03 of 1.62:l.
Results:
1. Of the 58 imaged casts, 10 (17%) had a perceived maxillary central:lateral incisor ratio of between 1.59 and 1.65:l. The mean perceived maxillary central:lateral incisor ratio was 1.51:l.
2. No cast had a perceived maxillary lateral incisor:maxillary canine ratio within the 1.59-1.65:l range.
3. The mean maxillary central:mandibular central incisor ratio was 1.58:l and the range was 1.42-1.8O:l.
Concerns:
– A cast of teeth lacking the 1:0.618 ratio still appears to fit the Levin grid.
• The caliper tips were too large to permit accurate inter-proximal placement.
Discussion:
The results of the study denied the existence of ratios such as the golden proportion in the average natural dentition.
Conclusion
The golden proportion was found in the relationship between the perceived width of the maxillary central and lateral incisors in 17% cases.


