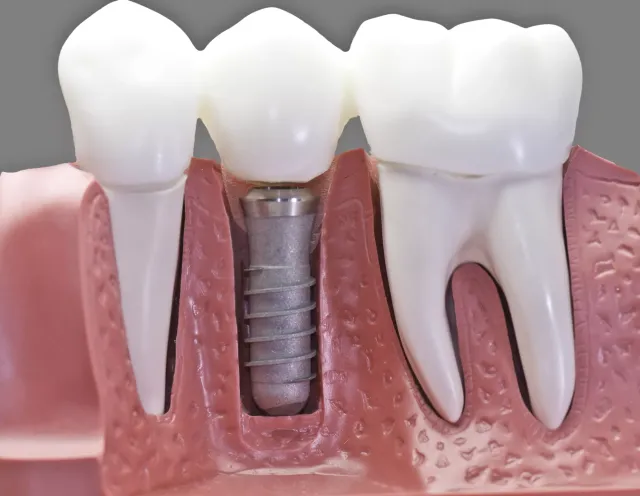
- By - Malfaifi
- Posted on
- Posted in Uncategorized, زراعة الاسنان
Heat-induced bone injury
Tremperature threshold levels for heat-induced bone injury: A vital-microscopic study in the rabbit
Eriksson and Albrektsson 1983

- Critical temperature is to be around 56° because alkaline phosphate denatured at this temperature level.
- Hard tissue changes after heating in the range of 47° to 50 c.
- The heating was performed about 10 weeks liter chamber insertion.
- Acute effects. A hyperemia was noted during heating. This increase in blood flow velocity was when the temperature was raised to 40* to 41° C higher.
- Long-term effects. The following changes in vessels, fat cells, and bone occurred as long-term effects.
- Daring further observation period of 40 to 50 days, only minor vascular changes such as a slight reorientation of the vessels occurred.
- Pat cells. Fat cell resorption usually started 2 days after heating with changes in the appearance of cells and a darkening of their color.
- An observation period of 30 to 40 days, about 30% of the bone was resorbed
- The increased blood flow was observed at a temperature of 40 c to 41° C.
- In the present study no permeability was observed.
- observation that a circulatory arrest was noted in some minor vessels after heating to ^0° C may imply that the threshold level for vascular survival is readied. at this temperature.
- Heating to of 60° C or more resulted in 2 permanent cessation of blood flow and an obvious bone tissue necrosis
- no signs of tissue recovery even over follow-up periods of 1 year.
- This study indicates that bone tissue is sensitive to heating at the level of 47” C in 1 min