- By - Malfaifi
- Posted on
- Posted in Fixed, Implant Dentistry, Prosthesis, Removable
Restorative space part 4 – Clinical considerations for increasing OVD
Clinical considerations for increasing occlusal vertical dimension: a review
J Abduo , K Lyons 2012
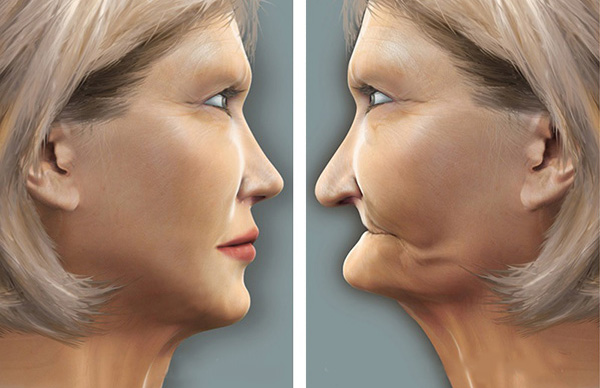
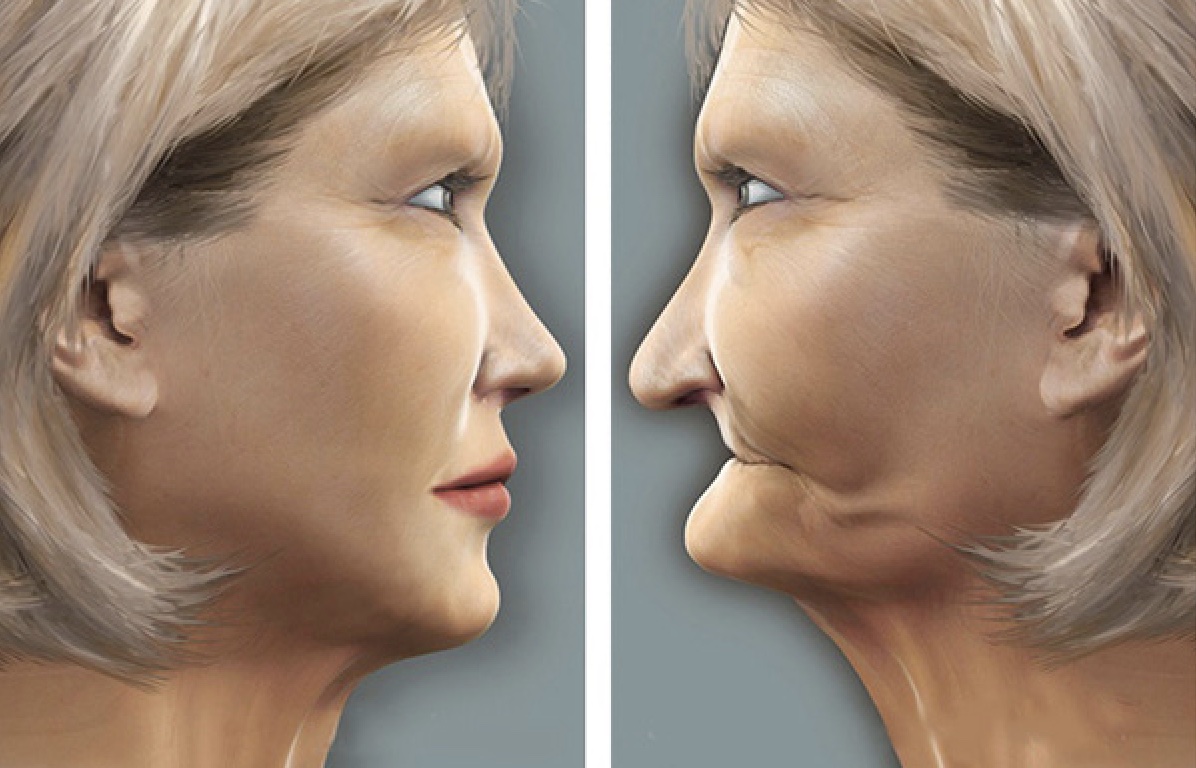
Occlusal vertical dimension : The distance between two selected anatomic points. JPT9
Consequences of increasing the OVD
Hyperactivity of the masticatory muscles
Elevation in occlusal forces
Bruxism
Temporomandibular disorders (TMDs).
Inter-occlusal rest space (IORS) of more than 2 mm indicates that the OVD can be safely increased. Turner
limitations associated with positioning the mandible at rest:
The same individual, different mandibular positions can be obtained at different examination periods. This has been attributed to the influence of muscle activity and fatigue.
The mandibular rest position occurs at a zone rather than a specific level.
This finding is supported by clinical studies that have confirmed the ability of the patient to adapt after increasing the OVD. Carlsson 1979
Variation between clinicians in evaluating the resting position of the mandible.
The determination of the OVD increase should not be based on IORS values. Carlsson 1979
It has been suggested that in order to improve the accuracy of the recording procedure, more than one method should be used.
Esthetics:
Fishman found that tooth wear resulted in a reduction of arch width and gonial angle that may contribute to the overall mandibular pseudo prognathism.
Loss of OVD and subsequent forward rotation of the mandible
An edge-to-edge anterior tooth relationship
Anterior positioning of the mandible due to the loss of anterior tooth guidance.
Is increasing the OVD reduces the pseudo-prognathism ?
Increasing the OVD for dentate individuals is limited to 5 mm inter-incisally, which may not be sufficient to induce facial alterations.
Gross et al. reported that after experimental increase of the OVD by 2–6 mm for dentate individuals, there was an insignificant extraoral improvement of facial tissues appearance.
Excessive display of the gingival tissues will not be improved by increasing OVD.
Temporomandibular joint status
It could be speculated that the development of TMD is not associated with the loss of OVD.
Stabilizing TMD patients and minimizing the signs and symptoms with a removable occlusal appliance before the commencement of irreversible prosthodontic treatment.
– Loss of posterior tooth support has been cited as probably the main cause for loss of OVD in dentate individuals.
– Patients with a steep anterior tooth guidance can benefit significantly from increasing OVD as it will alleviate the broad area of anterior tooth contacts and provide shallower and less constrained angle of disclusion.
– In relation to the magnitude of increasing the OVD, an increase of up to 5 mm inter-incisally is a feasible alteration
Dahl and Krogstad increased the OVD for 20 participants up to 4.7 mm by using anterior removable splints.
For implant supported prostheses, the only available study reported an extended period of grinding and clenching of up to three months. A possible explanation for this increased parafunctional activity is the lack of sensory feedback from the periodontal ligament that might hinder rapid patient adaptation after increasing OVD.