Restorative space
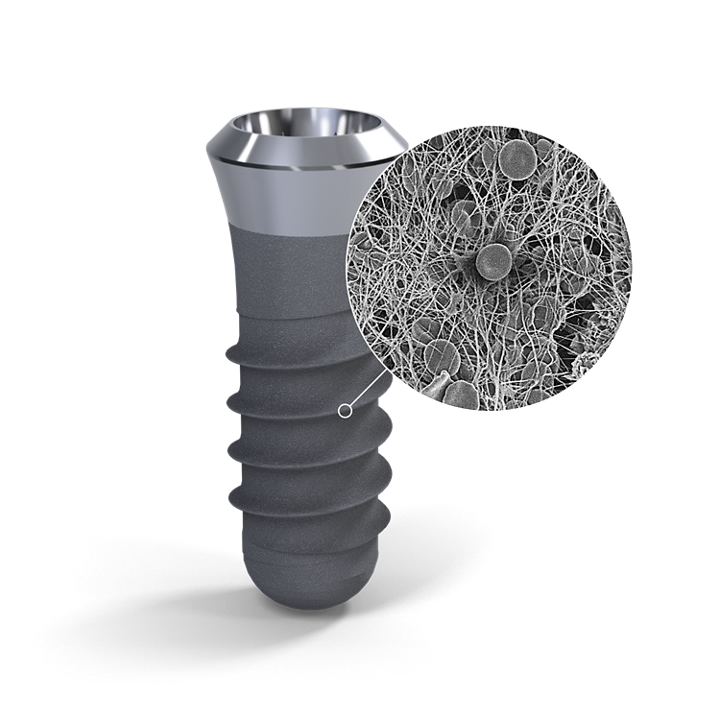
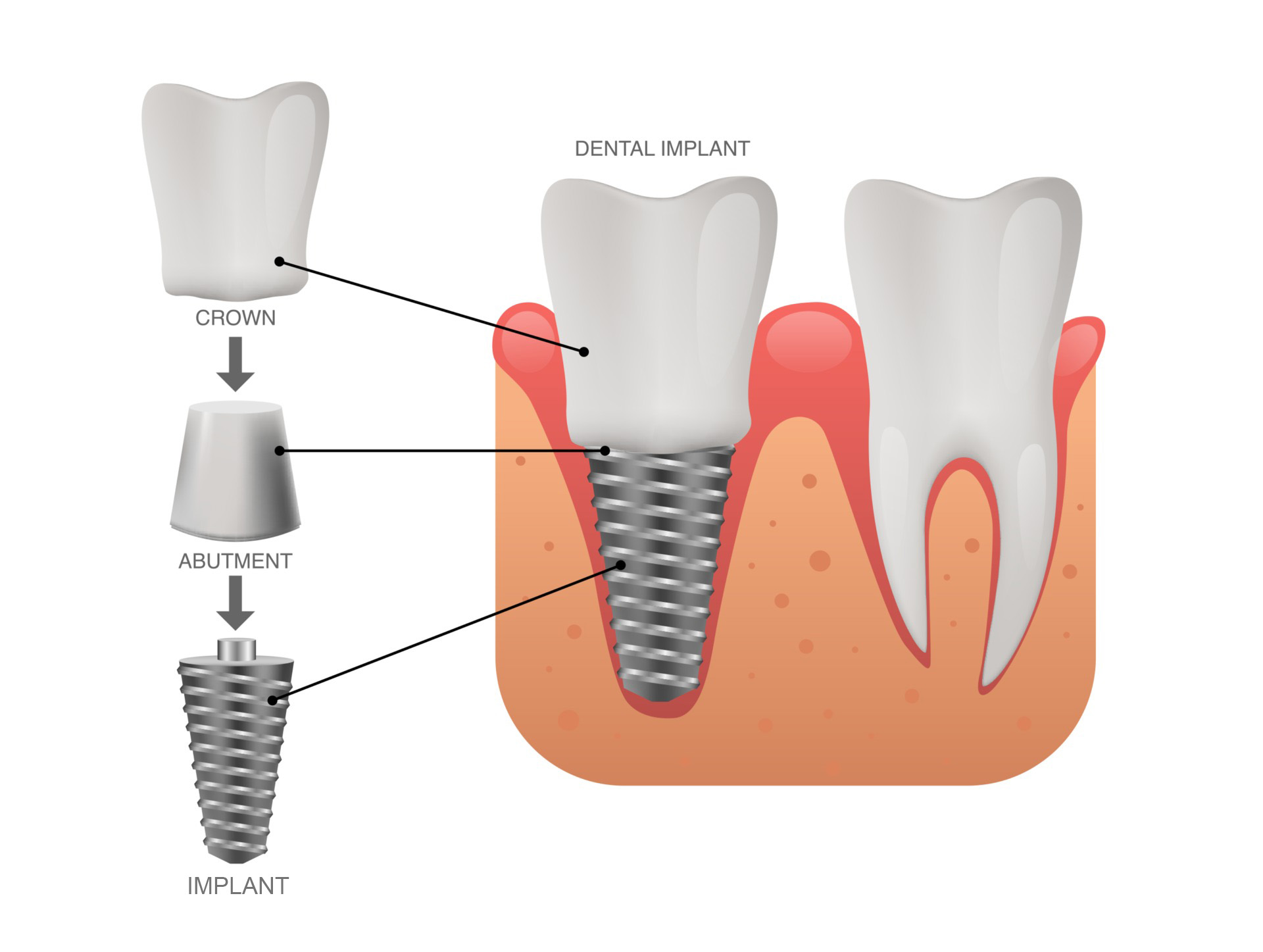
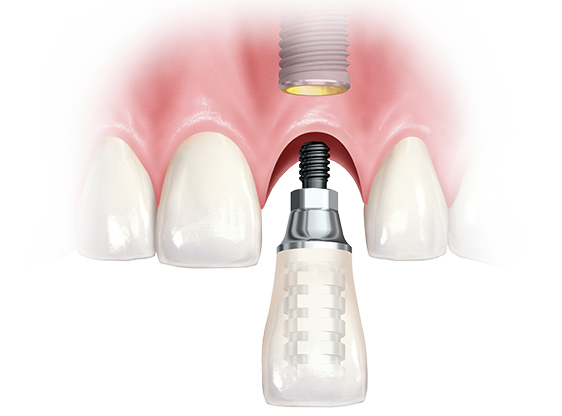
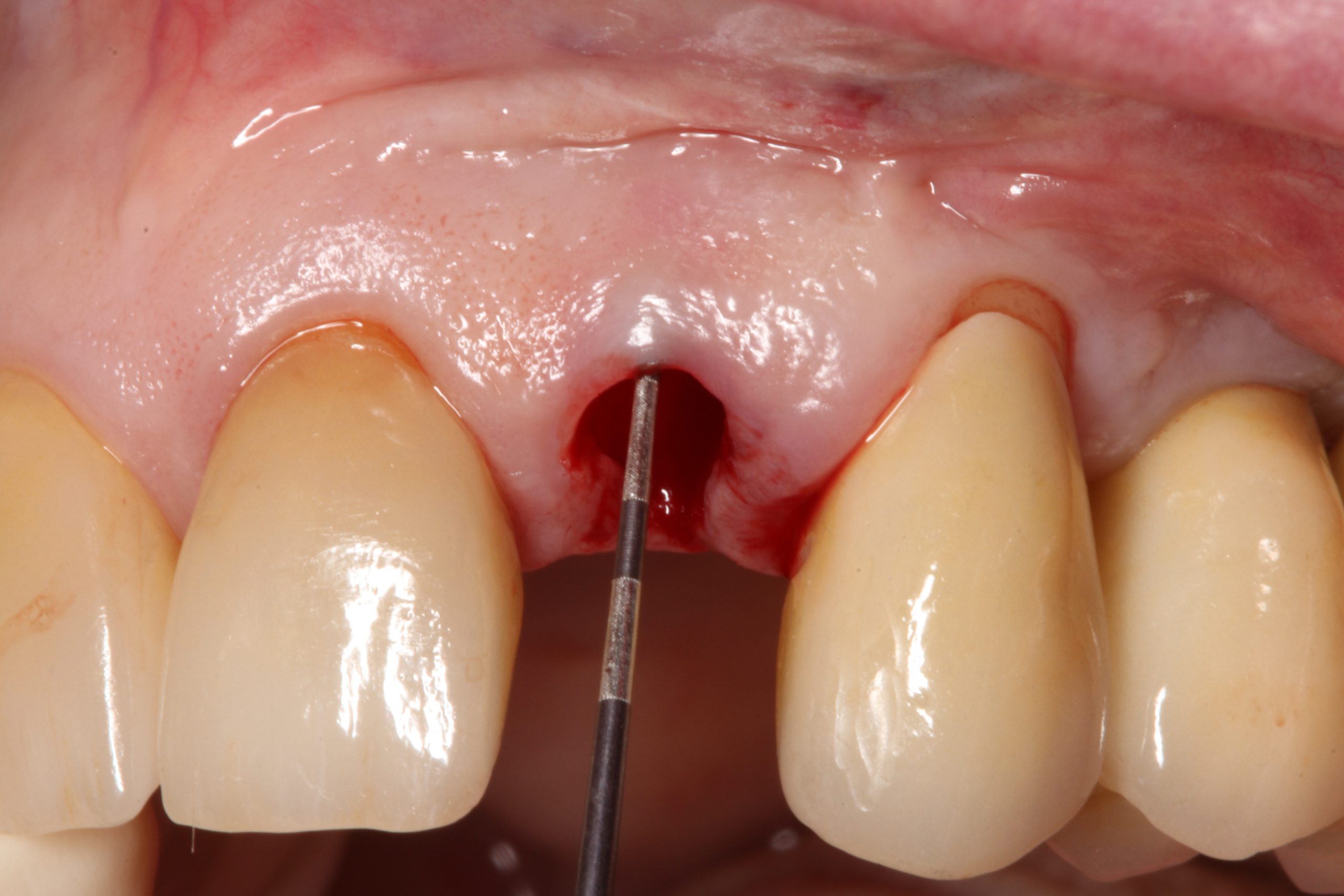
Restorative space – part 1 Vertical restorative space : Single screw/cemented implant supported crown, Implant supported fixed dental prosthesis screw/cemented Restorative Space definitions: Dental restorative space may be defined as the 3-dimensional oral space available for prosthodontic restoration. Ahuja et al, JPD 2011 The vertical distance between the maxillary and mandibular dentate or edentate arches.