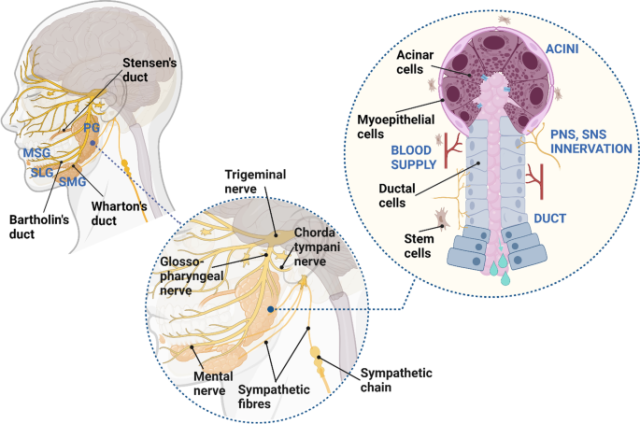
Xerostomia
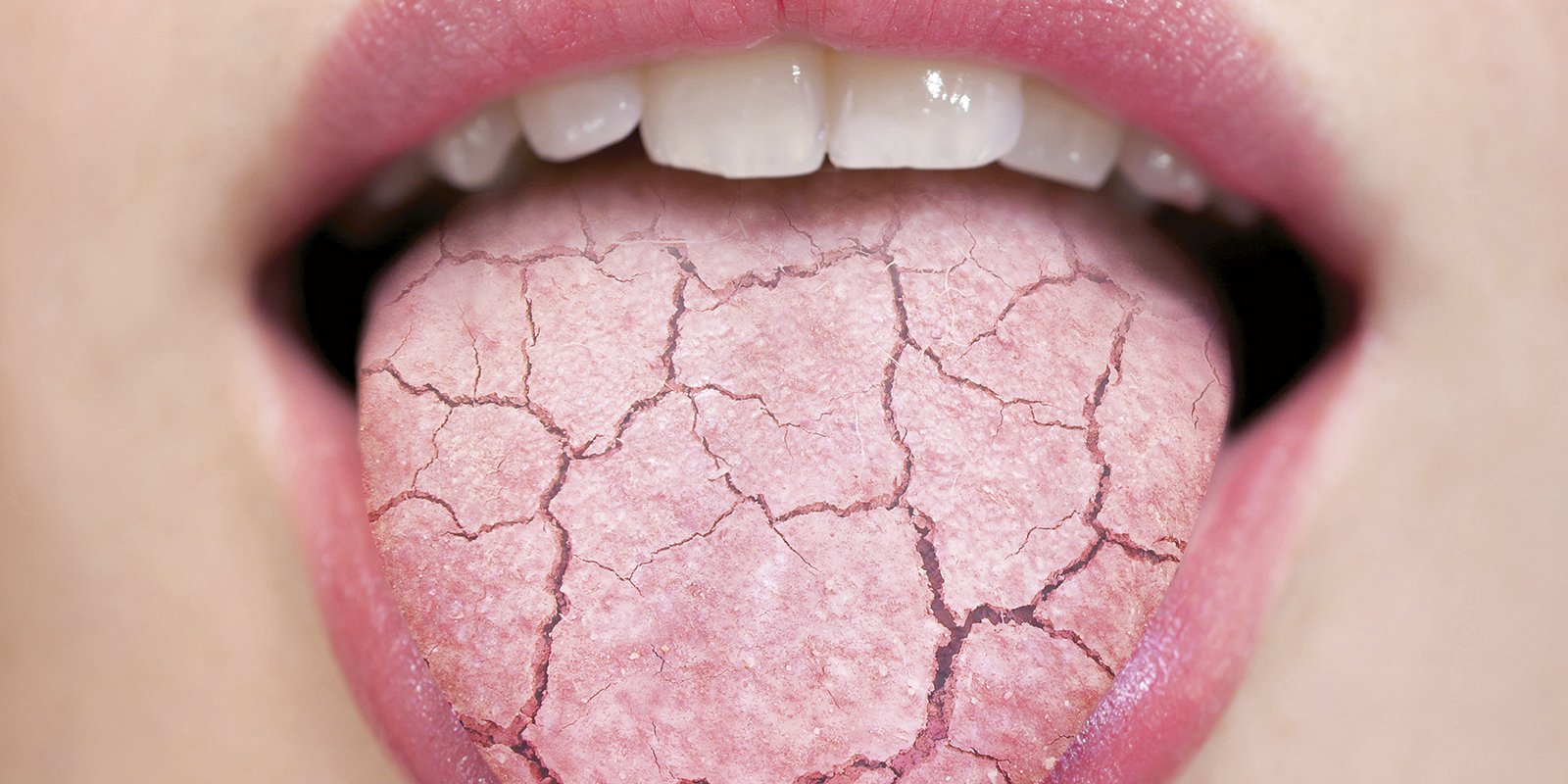
Hyposalivation and Xerostomia: Etiology, Complications, and Medical Management Turner 2016 · Hyposalivation: an objective finding of a decreased salivary production · Xerostomia: the subjective feeling of having dry mouth · Normal unstimulated flow rate: 800-1500 mL/day or 0.3-0.4 mL/min · Abnormal flow rate: <0.1 mL/min Normal Salivary Function · 2 components: mucinous and serous,